2019 Retrospect in Auto Industry in globe
2020/02/10 | By CENSA harsh economic situation swept through the global automotive market in 2018, largely due to slowing market demand and political competition among the world's superpowers, as well as decreasing confidence from consumers, leading to the first decline in five years in the industry. More importantly is how the main markets in China, Europe and North America have already fallen into negative growth. Despite the shrinking market, there are several promising prospects to expect, including exponential growth in electric vehicles and advancing self-driving car technologies.
Due to the shrinking auto markets in both China and the U.S., the sales in the global auto market in 2018 was down by 0.7% to 93.6 million units as other markets were unable to step in. Together with China's stimulus package and on the condition that the country maintains peaceful trade negotiation with the U.S. and other countries, the annual growth rate for 2019 is expected to be at 1%. However, if the trade negotiations between the U.S and China break down, the global auto market would face a difficult recovery between 2019 and 2021.
Not much changes were made to the global auto market distribution, with China still the largest market at 30% and followed by the U.S. with 19%. Together are influential in terms of global influence as both make up half of the world's auto market.
In 2018, the Chinese auto market suffered through a severe economic downturn. Although the government launched tax cuts and auto dealers lowered the price to stimulate consumer spending, both attempts failed to turn the market around.
On the other hand, sales in the U.S auto market were surprisingly steady in 2018, far beyond market prediction. The overall sales were approximately 17.30 million units, surpassing the record for over 17 million units sold in four consecutive years, representing the tenacity of the American auto manufacturing industry. However, with four factors disrupting the market-- increasing car loan interest rates, fewer car rental discount programs from auto plants, the economic cycle of the auto market, and more appealing options among second-hand cars --sales of new vehicles were impacted, prompting concerns of an overall market decline.
Self-Driving Vehicle Trends
Faced with the business opportunity and trends in the global autonomous vehicle industry, governments and industries compete to develop their vision and blueprint of their desired self-driving vehicles.
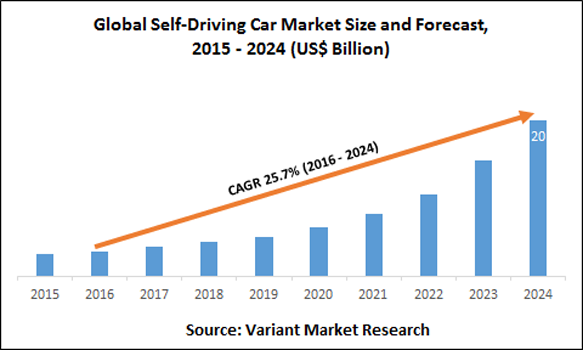
The development of self-driving cars in the European region is comparatively conservative, mainly focusing on self-driving business cars and medium-sized shuttle buses. With consideration of strict guidelines to upholding human dignity, safety and information protection standards and protocols, estimates of the region reaching Level 5 Self-Driving Vehicles is much more conservative, suggesting the goal could be reached after 2035.
In the Asian region, Japan offers a more comprehensive blueprint compared to its other Asian counterparts, primarily due to its aging society and the upcoming Tokyo Olympics in 2020. Japan has chosen to focus on developing an autonomous vehicle fleet and increased, stringent, safer driver assistance systems. In the short-term, Japan aims to offer public transportation services and highway driving in accordance with NHTSA Level 3 standards ahead of the Tokyo Olympics, while in the long-term, realize Level 5 full automation capabilities after 2030. China has also invested in the research of self-driving car-related technology and prompted legislation revision in 2017 under government agencies like the Ministry of Transportation, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, and Ministry of Public Security in Beijing. With the regulation and enforcement self-driving vehicle laws underway, China aims to realize Level 4 capabilities on the highway after 2025.
Taiwan's Position and Outlook in the Auto Industry
Taiwanese manufacturers not only have the ability to design quality products, manage the factories, while they keep flexible manufacturing all the while maintaining quality. These firms have been exporting products to the U.S. and Europe for many years, maintaining tight-knit supply chains from up-stream to downstream in the auto industry, especially buoyed by the advantages of having a strong, domestic ICT industry. Taiwan's private ICT companies such as TMSC, Winbond, MediaTek, Foxconn, and Delta have tapped in the autotronics field with its steady manufacturing capabilities, gradually forming the stepping stones for a comprehensive supply chain under a domestic self-driving vehicle industry.
On the other hand, the government is actively pushing for the legislation of related regulations for self-driving vehicle oversight. The Industrial Technology Research Institute has predicted the global market value for markets such a self-driving cars, connected cars, electric cars and would reach an estimated US$800 billion by 2030. The institution also holds expectations to see Taiwan build a strong production chain by integrating automotive software and hardware, and thus, cement its role in the emerging markets.